“Aquaponic Gardening” is a comprehensive guide for growing vegetables and fish together efficiently. It provides step-by-step instructions for setting up and maintaining a successful aquaponic system.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced gardener, this book offers valuable insights and practical tips for achieving a thriving aquaponic garden. By combining aquaculture and hydroponics, aquaponic gardening is a sustainable and eco-friendly way to cultivate fresh produce and fish in a symbiotic environment.
This guide covers everything from selecting the right fish and plants to optimizing water quality and nutrient levels, making it a must-read for anyone interested in sustainable food production. Get ready to dive into the world of aquaponics and unlock the potential of this innovative gardening technique.
Introduction To Aquaponic Gardening
Aquaponic gardening combines aquaculture and hydroponics, allowing you to grow vegetables and fish together in a closed system. Our step-by-step guide provides the necessary information to start your own aquaponic garden, including choosing the right fish and plants, setting up the system, and maintaining it for optimal growth.
A Symbiotic Relationship
In the world of gardening, aquaponic gardening stands out as a remarkable system that combines the cultivation of plants and the rearing of fish in a harmonious and mutually beneficial way. This unique method of gardening utilizes a symbiotic relationship between aquatic animals and plants to create a sustainable and efficient ecosystem. The fish provide the necessary nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter and purify the water for the fish. It’s a win-win situation where both the fish and the plants thrive together.
Benefits For Modern Agriculture
Aquaponic gardening offers numerous benefits for modern agriculture that make it an attractive option for both hobbyists and commercial growers. Firstly, this system requires significantly less water compared to traditional farming methods. The water in the system is continuously recycled, reducing water consumption by up to 90% compared to conventional farming.
Secondly, aquaponics eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, making it an environmentally friendly and sustainable approach to gardening. The fish waste provides the necessary nutrients for the plants, eliminating the need for synthetic fertilizers. Additionally, the plants’ roots act as a natural filter, removing harmful substances from the water and creating a healthy environment for the fish.
Furthermore, aquaponics allows for year-round cultivation, regardless of the climate or season. The controlled environment in which the system operates provides optimal conditions for plant growth, allowing for a continuous harvest of fresh produce. This not only ensures a steady supply of vegetables but also reduces the dependence on imported or out-of-season produce.
Lastly, aquaponic gardening promotes self-sufficiency and food security. By growing your own vegetables and raising fish, you have control over the quality and safety of your food. This method also reduces reliance on external food sources, making it a viable option for communities and regions with limited access to fresh produce.
In conclusion, aquaponic gardening offers a sustainable and efficient approach to cultivating vegetables and rearing fish. The symbiotic relationship between the plants and fish creates a harmonious ecosystem that requires less water, eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers, allows for year-round cultivation, and promotes self-sufficiency. Whether you are a gardening enthusiast or a commercial grower, aquaponics can revolutionize the way you grow your food.
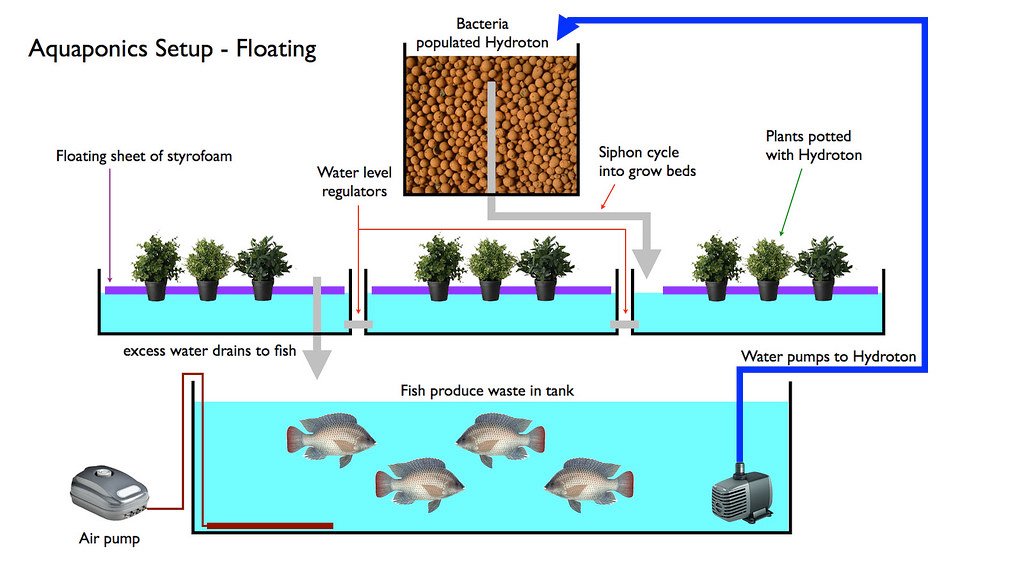
The Basics Of Aquaponics
Discover the fundamentals of aquaponics through a step-by-step guide on combining vegetable cultivation and fish farming. Learn how this sustainable method creates a harmonious ecosystem for plants and aquatic life, offering a unique and efficient approach to gardening. Gain insights on the interconnected relationship between plants and fish, fostering a thriving environment.
Your Attractive Heading
Aquaponics is a sustainable system that combines hydroponic gardening and aquaculture, allowing you to grow vegetables and fish in one integrated system. The basic components of an aquaponic system include the fish tank, grow beds, water pump, and plumbing system. The fish tank is where you raise fish, while the grow beds are where your plants grow. The water pump moves water from the fish tank to the grow beds and back again, while the plumbing system connects all the components together.
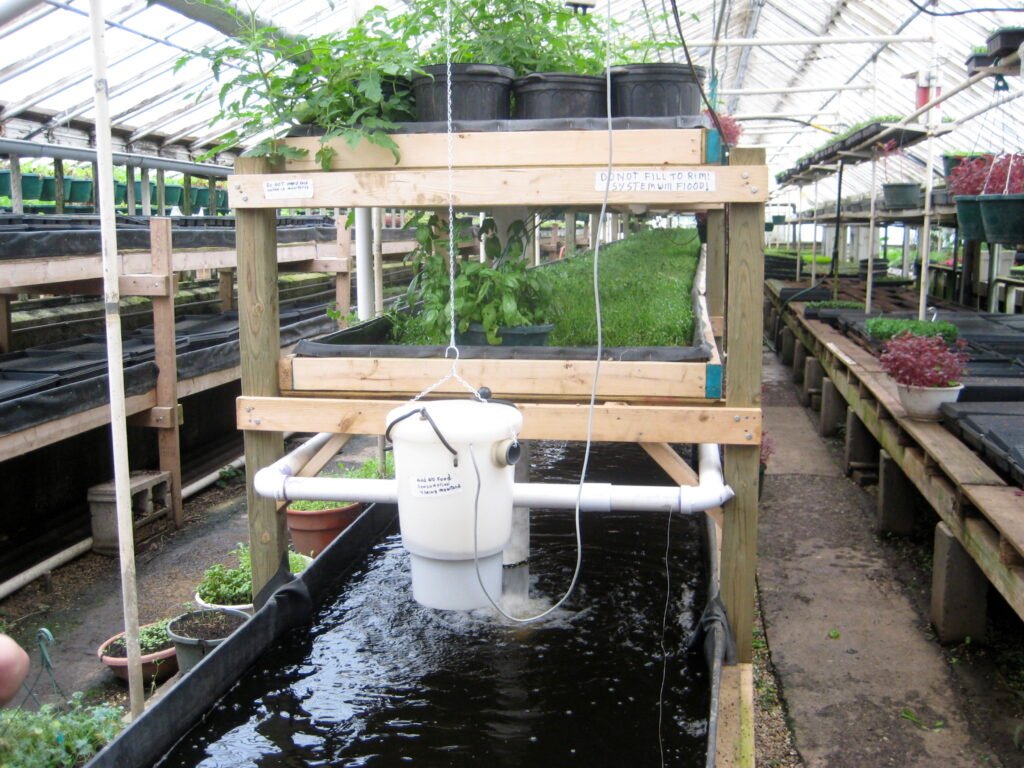

Key Components
Aquaponics is a sustainable system that combines hydroponic gardening and aquaculture, allowing you to grow vegetables and fish in one integrated system. The basic components of an aquaponic system include the fish tank, grow beds, water pump, and plumbing system. The fish tank is where you raise fish, while the grow beds are where your plants grow. The water pump moves water from the fish tank to the grow beds and back again, while the plumbing system connects all the components together.
The Nitrogen Cycle Explained
The nitrogen cycle is the most crucial aspect of aquaponics. Fish produce waste, which contains ammonia. Ammonia is toxic to fish, but it’s an excellent source of nitrogen for plants. In an aquaponic system, bacteria convert ammonia into nitrite and then nitrate. Nitrate is a form of nitrogen that plants can absorb and use to grow. The plants in the grow beds filter the water and remove the nitrate, which is then returned to the fish tank. This cycle of waste to plant food to clean water is what makes aquaponics so sustainable and efficient. To summarize, the key components of an aquaponic system include the fish tank, grow beds, water pump, and plumbing system. The nitrogen cycle is the process that allows fish waste to be converted into plant food, which in turn cleans the water for the fish. By understanding these basics, you can start your aquaponic gardening journey with confidence.
Setting Up Your Aquaponic System
Aquaponic gardening is a sustainable and efficient way to cultivate both plants and fish in a single, integrated system. Setting up your aquaponic system is a crucial first step towards a successful and thriving garden. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process, covering everything from selecting the right location to assembling the necessary equipment.
Choosing The Right Location
When selecting a location for your aquaponic system, consider factors such as sunlight exposure, accessibility to water and power sources, and proximity to your living space. Ensure the area has ample natural light for the plants to thrive and is sheltered from extreme weather conditions. Additionally, make sure the location allows for easy access to water and power supplies to support the functioning of the system.
Equipment Checklist
Before diving into the setup process, it’s essential to gather all the necessary equipment for your aquaponic system. Check off each item from the following checklist to ensure you have everything needed to proceed:
- Aquarium or fish tank
- Grow bed or media bed
- Water pump
- Air pump and air stones
- Plumbing fittings and tubing
- Grow lights (if growing indoors)
- pH testing kit
- Net pots or plant containers
Selecting Your Fish And Plants
A crucial step in aquaponic gardening is selecting the right combination of fish and plants to create a thriving ecosystem. By carefully choosing the best fish for aquaponics and the ideal plants to grow, you can ensure a harmonious environment where both elements support each other’s growth.
Best Fish For Aquaponics
When choosing fish for your aquaponic system, it’s essential to consider their compatibility with the plants you want to grow. Some of the best fish species for aquaponics include:
- Tilapia
- Trout
- Catfish
- Goldfish
Ideal Plants To Grow
Equally important is selecting the right plants that thrive in an aquaponic environment. Some ideal plants to grow in aquaponics systems are:
- Lettuce
- Basil
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
Maintaining Your Aquaponic Garden
Discover the essentials of maintaining your aquaponic garden in this step-by-step guide to raising vegetables and fish together. Learn how to ensure the optimal health of your aquatic ecosystem, balance the nitrogen cycle, and troubleshoot common issues for a thriving and sustainable aquaponic setup.
Maintaining Your Aquaponic Garden Monitoring Water Quality Regularly check pH levels, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates in the water. Use a test kit to monitor water parameters at least once a week. Adjust pH levels to keep the water in the optimal range for both plants and fish. Feeding Your Fish Feed your fish a balanced diet of commercial fish food. Do not overfeed the fish to prevent water quality issues. Monitor fish behavior to ensure they are eating properly. In aquaponic gardening, maintaining your system is crucial for the health of both your plants and fish. Monitoring water quality is essential to ensure a thriving ecosystem. Use a test kit to check pH levels, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates regularly. Adjust pH levels when needed to keep the water conditions optimal for your plants and fish. When it comes to feeding your fish, it’s important to provide them with a balanced diet. Use commercial fish food and avoid overfeeding to prevent water quality issues. Monitor your fish’s behavior to ensure they are eating properly. A well-fed fish will contribute to the overall health of your aquaponic system.

Common Challenges And Solutions
Aquaponic gardening presents unique challenges, including maintaining proper water pH levels and preventing fish waste buildup. Solutions involve testing and adjusting water parameters regularly, and implementing efficient filtration systems to ensure a healthy environment for both plants and fish.
Common Challenges and Solutions: Aquaponic gardening is a sustainable and efficient way of growing plants and fish together. However, like any other gardening technique, it also has some common challenges. In this section, we will discuss the common challenges faced by aquaponic gardeners and their solutions. Dealing with Pests: Pests can be a major problem in aquaponic gardening as they can harm both the plants and fish. The most common pests in aquaponic gardens are aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. To deal with them, you can use natural pest control methods such as introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and praying mantis. You can also use organic insecticides made from natural ingredients like neem oil, garlic, and soap. Managing Algae Growth: Algae growth is a common problem in aquaponic gardens, and it can lead to reduced oxygen levels and fish death. The best way to manage algae growth is to prevent it from occurring in the first place. You can do this by controlling the amount of light that enters the system, reducing the amount of fish food, and adding algae-eating fish like tilapia and catfish. You can also use natural methods like adding barley straw or installing an ultraviolet sterilizer to prevent the growth of algae. In conclusion, dealing with pests and managing algae growth are the most common challenges faced by aquaponic gardeners. By using natural pest control methods and managing the amount of light and fish food, you can prevent these challenges from occurring. Additionally, adding beneficial insects and algae-eating fish can also help in maintaining a healthy and balanced aquaponic system.
Harvesting Your Bounty
Aquaponic gardening offers the unique opportunity to simultaneously cultivate both fish and vegetables in a sustainable and symbiotic ecosystem. As your aquaponic system matures, the time will come to reap the rewards of your hard work by harvesting your bounty. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process.
When To Harvest Fish
When the fish have reached their optimal size for consumption, it’s time to harvest them. This typically occurs after 6-12 months, depending on the species. Keep an eye on their growth and consult aquaculture experts to determine the best time for harvesting.
Tips For Harvesting Plants
- Harvest leafy greens such as lettuce and spinach when they reach full size, typically within 4-6 weeks of planting.
- Root vegetables like carrots and beets should be harvested when they have reached a desirable size, usually around 2-3 months after planting.
- For fruiting plants such as tomatoes and peppers, wait until the fruits are fully ripe before harvesting.
- Use sharp, clean scissors or pruning shears to carefully cut the plants, ensuring minimal damage to the rest of the crop.
- Handle harvested plants gently to prevent bruising and maintain their quality.
- Immediately transfer harvested plants to a cool, shaded area to preserve freshness.
Innovations In Aquaponic Gardening
Aquaponic gardening has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, with innovations in technology and a surge in community and urban projects. These developments have transformed the landscape of aquaponics, making it more accessible and efficient for both hobbyists and commercial growers.
Advancements In Technology
The integration of technology has revolutionized the way aquaponic systems are designed and managed. From automated monitoring and control systems to the use of advanced sensors and data analytics, technology has streamlined the process of maintaining optimal conditions for both plants and fish in aquaponic setups. The incorporation of energy-efficient LED lighting has also proven to be a game-changer, providing tailored light spectra for different plant species while minimizing energy consumption.
Community And Urban Projects
The rise of community and urban aquaponic projects has fostered a collaborative approach to sustainable food production. These initiatives have not only contributed to local food security but have also served as educational platforms, promoting the principles of aquaponics and fostering a sense of environmental stewardship within urban communities. By repurposing underutilized urban spaces, such as rooftops and vacant lots, these projects have demonstrated the potential for aquaponics to thrive in non-traditional settings, bringing fresh produce and fish to urban dwellers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Method Of Raising Both Fish And Vegetables?
Aquaponics is a method of raising both fish and vegetables in a symbiotic environment. The fish produce waste, which is converted into nutrients for the plants to grow. The plants, in turn, filter the water for the fish. This allows for a sustainable and efficient system of farming.
How To Grow Vegetables With Fish?
To grow vegetables with fish, follow these steps: 1. Set up an aquaponics system, where fish waste provides nutrients for plants. 2. Choose fish species that thrive in aquaponics, like tilapia or trout. 3. Maintain proper water quality and temperature for both fish and plants.
4. Provide adequate lighting and nutrients for plant growth. 5. Harvest your vegetables when ready for consumption.
What Types Of Fish And Vegetables Can Be Grown Using Aquaponics?
Aquaponics can grow various fish like tilapia and vegetables such as lettuce, herbs, tomatoes, and peppers.
How Many Fish Do You Need Per Plant For Aquaponics?
For aquaponics, a general rule is to have a ratio of 1 fish per plant. This ensures a balanced ecosystem where the fish provide nutrients for the plants through their waste. However, the specific fish-to-plant ratio can vary depending on factors like fish species, plant type, and system size.
Conclusion
Aquaponic gardening offers a sustainable and efficient way to grow both vegetables and fish together. By harnessing the natural symbiotic relationship between plants and fish, this method eliminates the need for conventional soil-based gardening and chemical fertilizers. With a step-by-step guide, you can easily set up your own aquaponic system and enjoy the benefits of fresh produce and fish while minimizing environmental impact.
Explore the world of aquaponics and unlock the potential of this innovative gardening technique today.





